- 1. Highlights of HMPA
- 2. Data sources
- 3. Usage of HMPA
- 4. Contact us
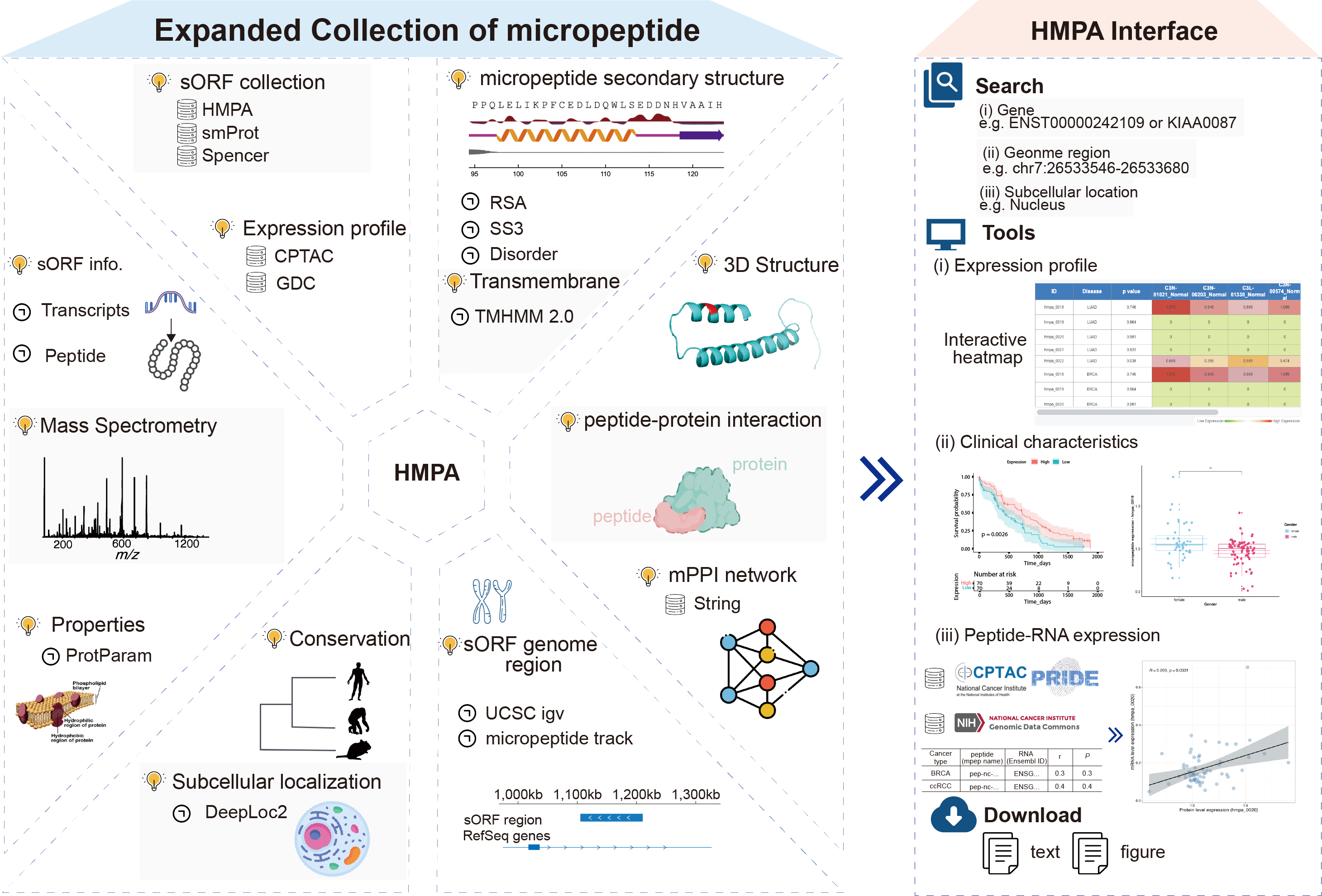
In the dynamic field of cancer research, the emerging study of micropeptides significantly enhances our understanding of tumorigenesis. The introduction of the Human Cancer Micropeptide Atlas (HMPA) marks a critical advancement, establishing a comprehensive database designed to decode the complex roles of micropeptides in cancerous tissues.
Utilizing state-of-the-art methodologies and extensive data integration, HMPA meticulously indexes millions of potential short open reading frames (sORFs) across various omics fields. The application of advanced technologies and stringent validation protocols ensures the robustness and accuracy of the HMPA dataset, providing a reliable resource for ongoing scientific exploration.
The HMPA database offers profound insights into disease-associated micropeptides and their correlations with patient outcomes, highlighting the significant influence of 19,586 non-classical proteins on cancer progression. Through predictive structural modeling and advanced bioinformatics analysis, HMPA explores the complex interactions of micropeptides within the oncogenic network.
As we advance in cancer research, HMPA’s dedication to continual updates and enhancements promises new opportunities in the study of micropeptides, potentially leading to innovative therapeutic strategies for cancer treatment.
We provide detailed list of sORFs results and spectral information. Please move to the “Download” page.
The abbreviations in the table below represent the names of various diseases. For the sake of convenience in referencing and identification, these disease names have been abbreviated. Please refer to the table to understand the specific diseases represented by each abbreviation.
| Tissue/cell lines | Cases by Disease Type | Abbreviation |
| Stomach | Gastric Cancer | GC |
| Colorectal | Colon Adenocarcinoma | COAD |
| Ovary | Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma | OV |
| Uterus | Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma | UCEC |
| Kidney | Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma | ccRCC |
| Lung | Lung Adenocarcinoma | LUAD |
| Breast | Breast invasive carcinoma | BRCA |
| Pancreas | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma | PDAC |
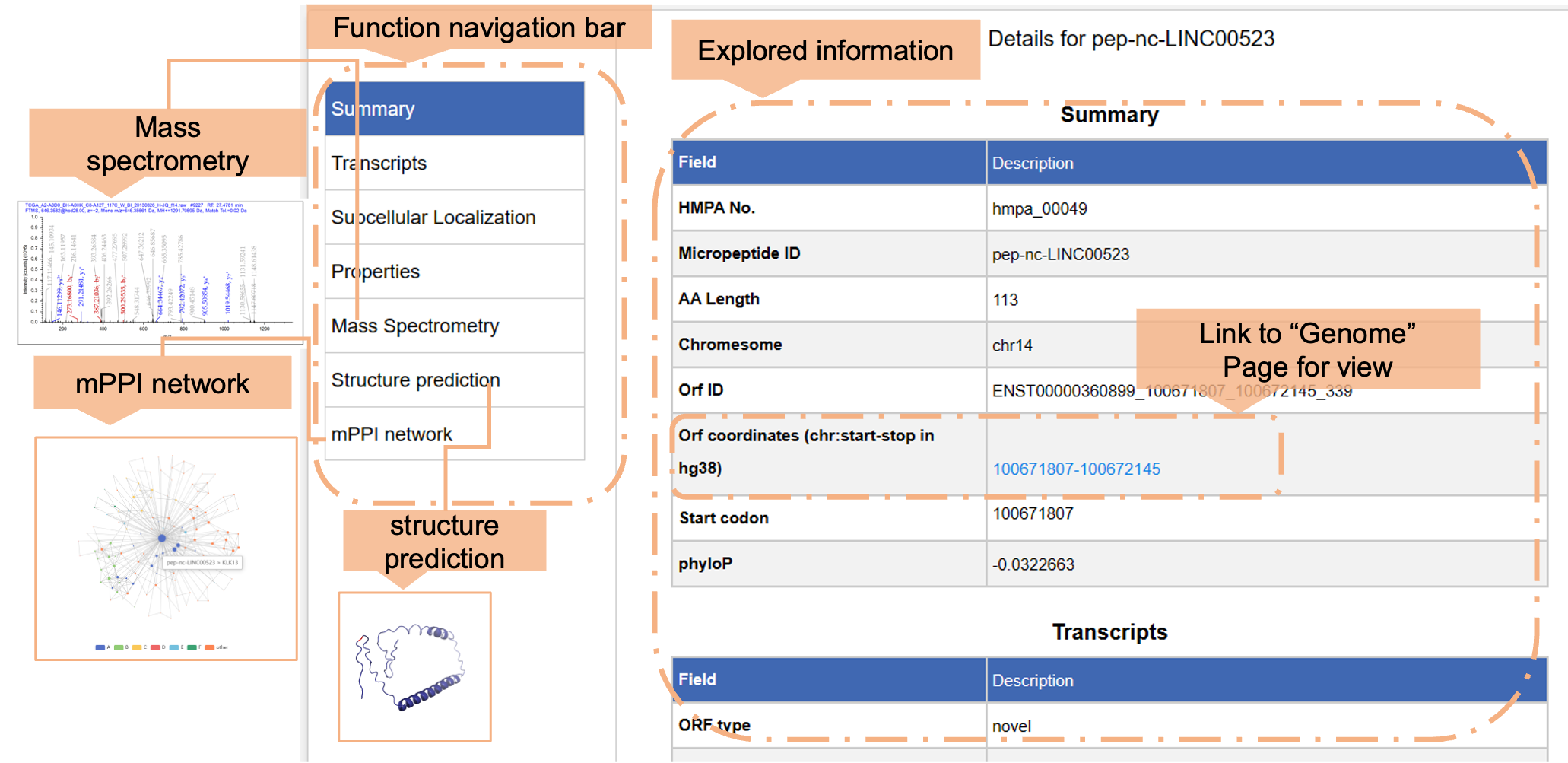
a) Explore micropeptide by ID globally
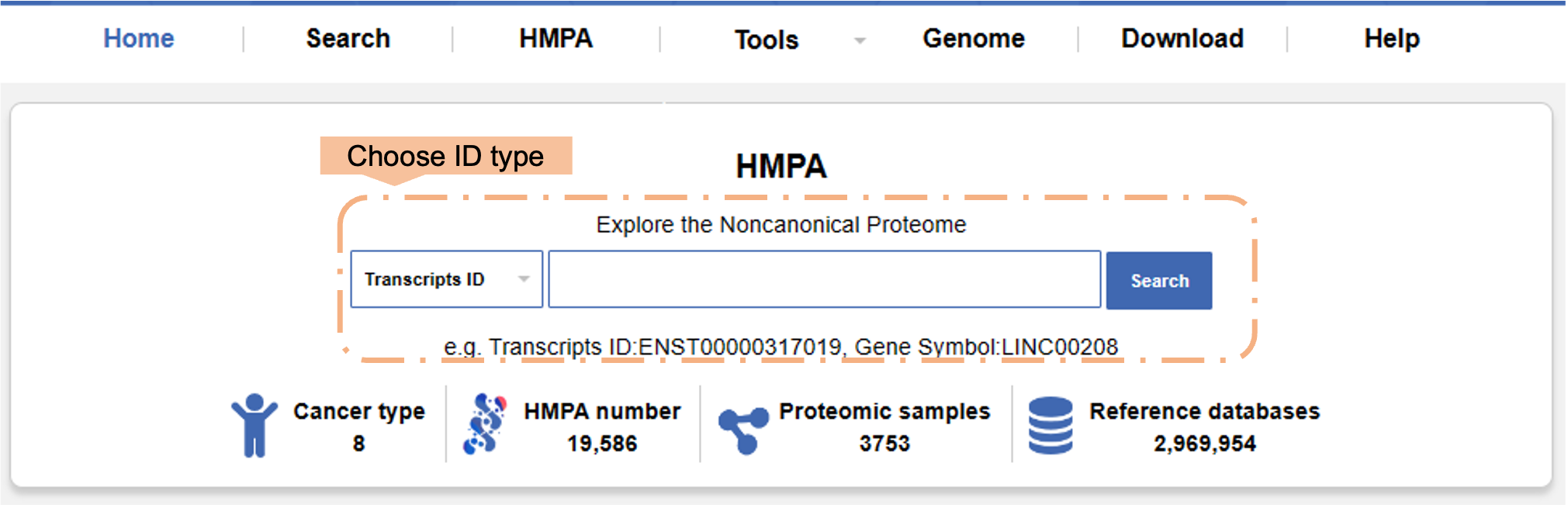
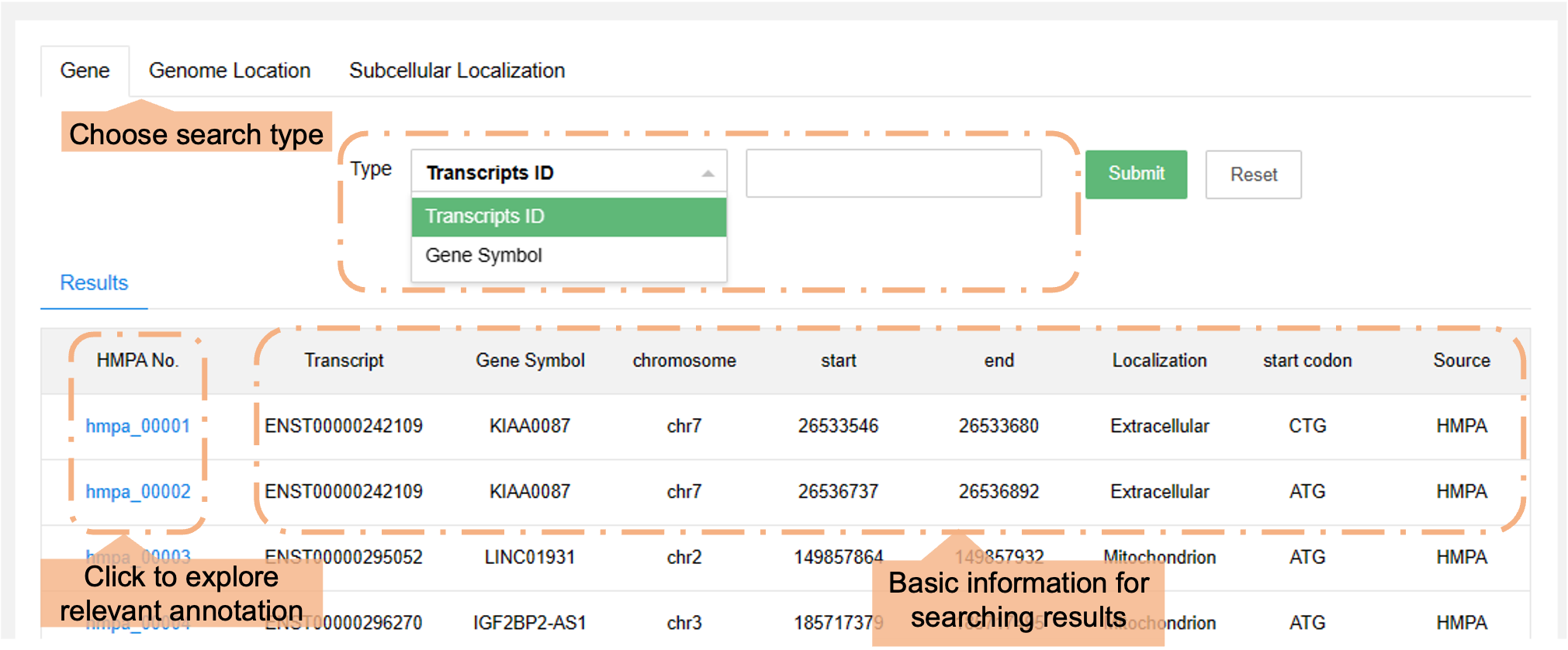
b) Explore micropeptides by utilizing Ensembl ID, genomic coordinates (GRCh38/hg38), or subcellular localization. The filtered information will be displayed in the “Results” section below.
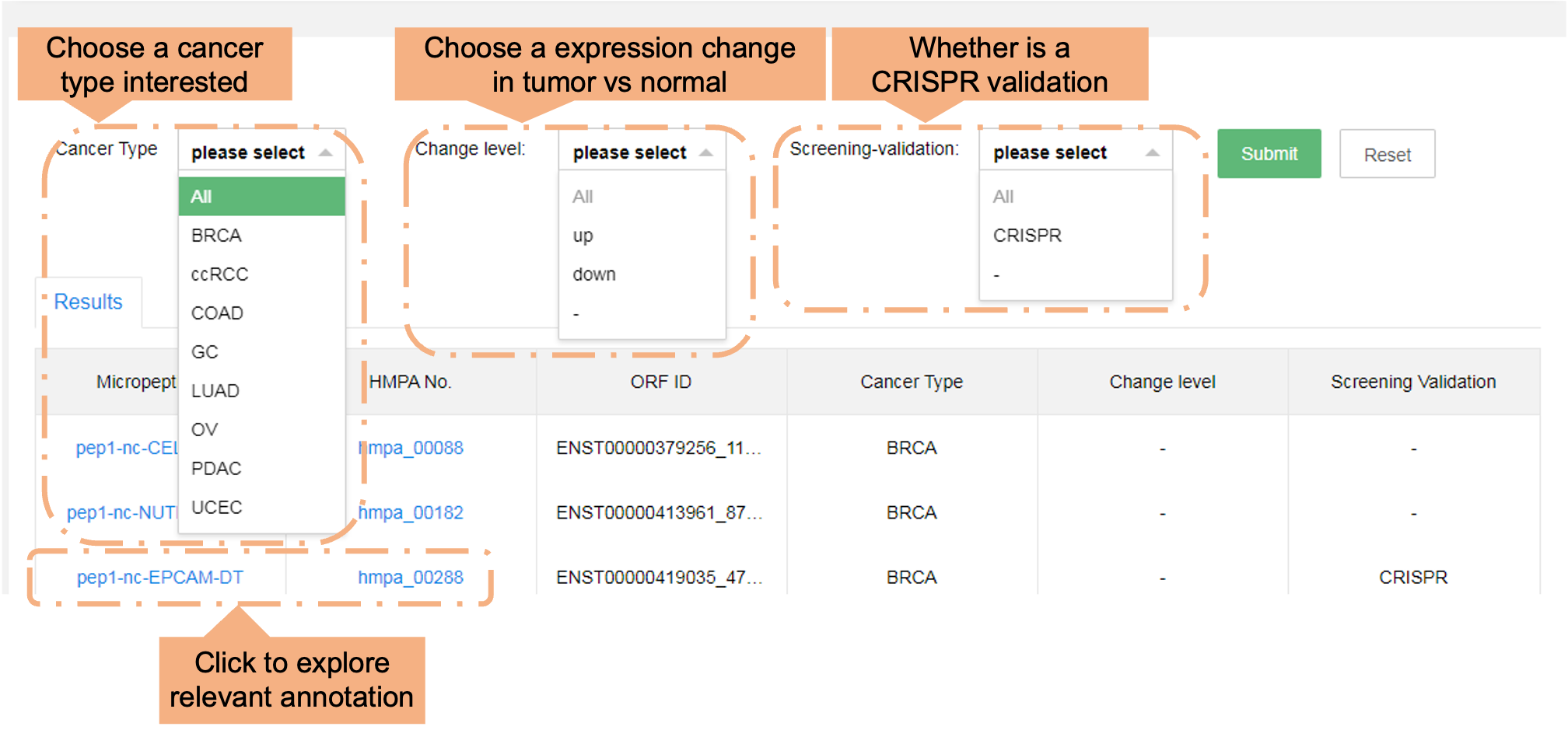
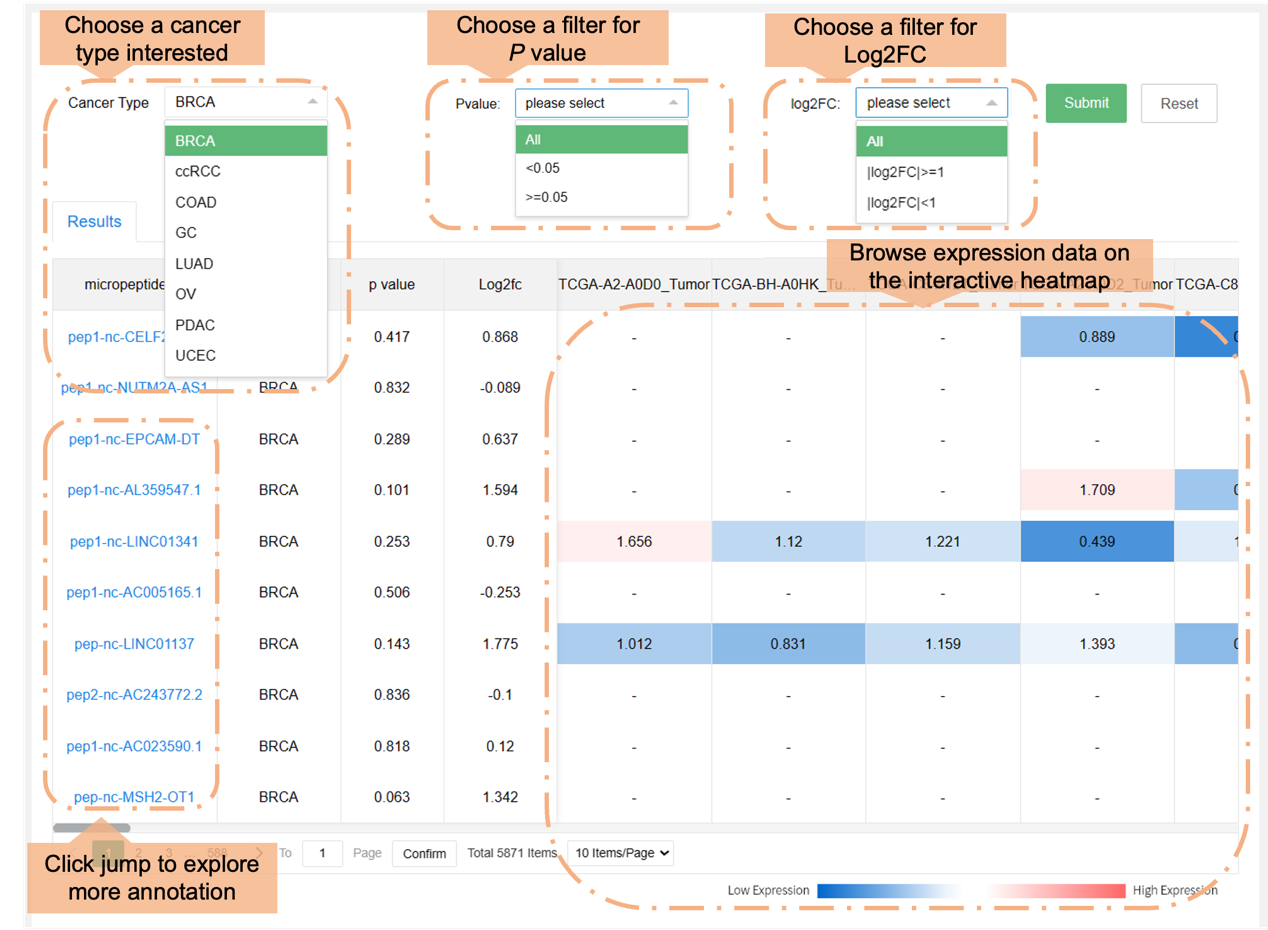
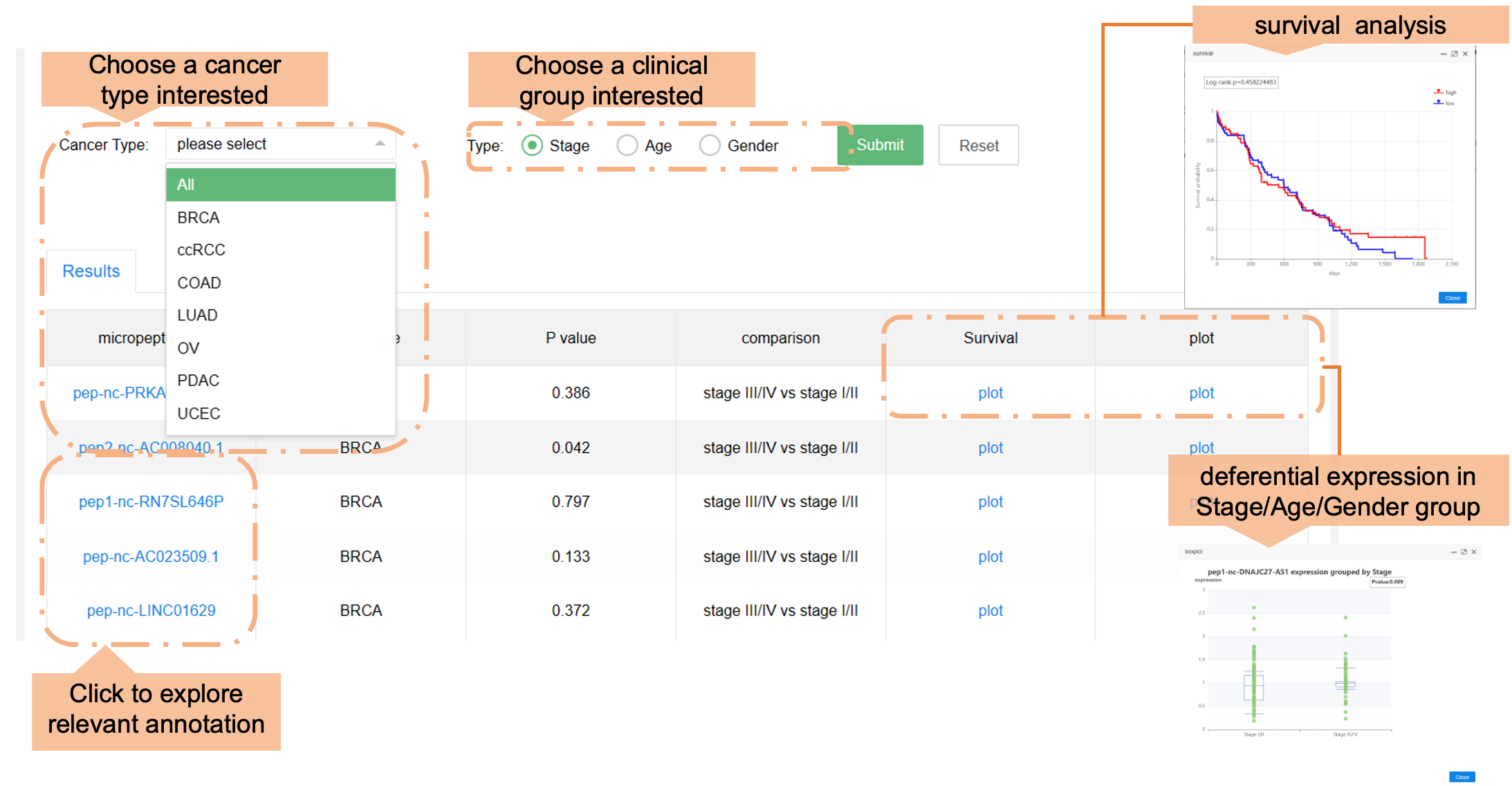
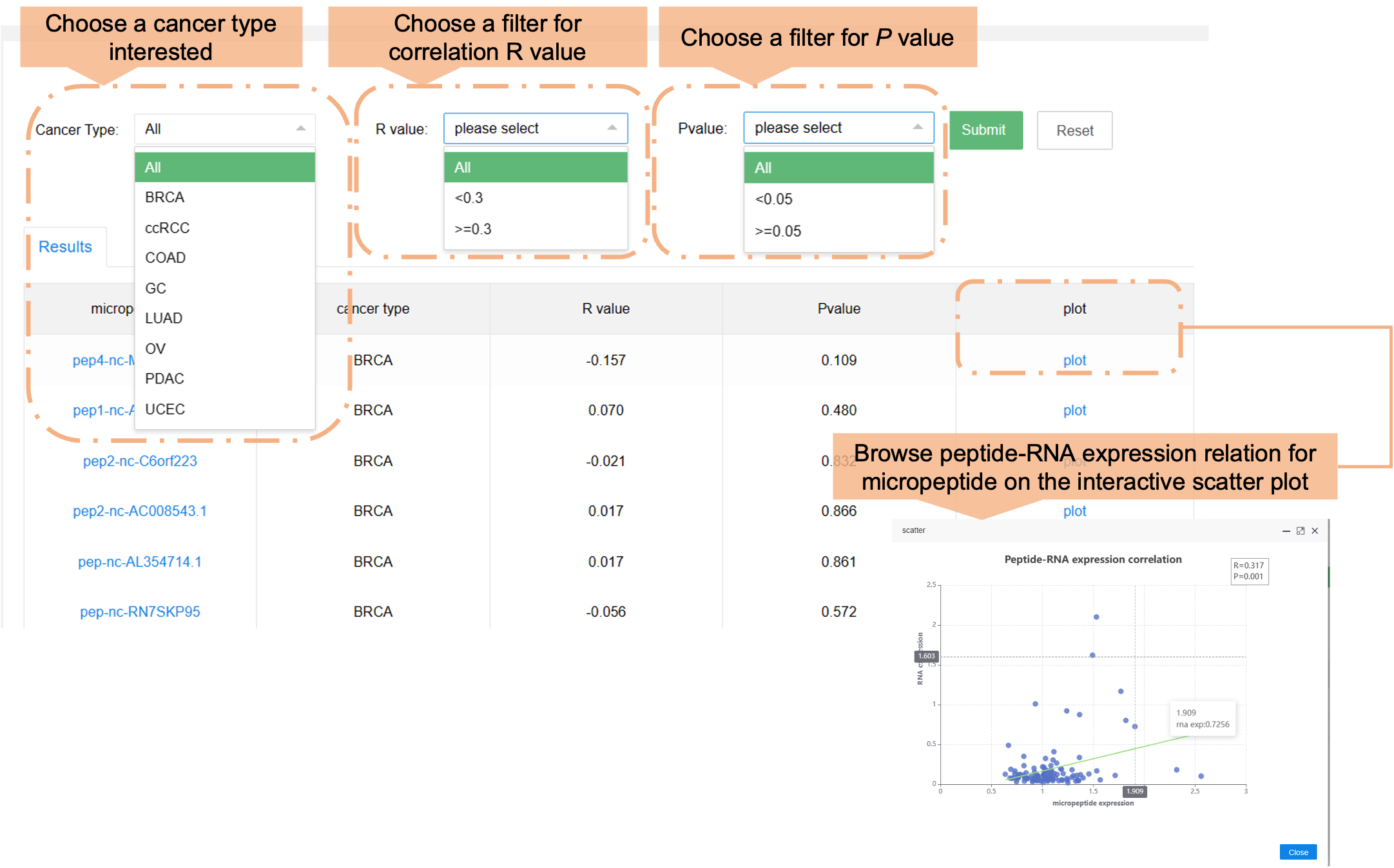
Users can browse the data in the HMPA by choosing various cancer types, or if they are differentially expressed. The section below labeled "Results" shows general information.
a) Expression profile
b) Clinical characteristics
c) Peptide-RNA correlation
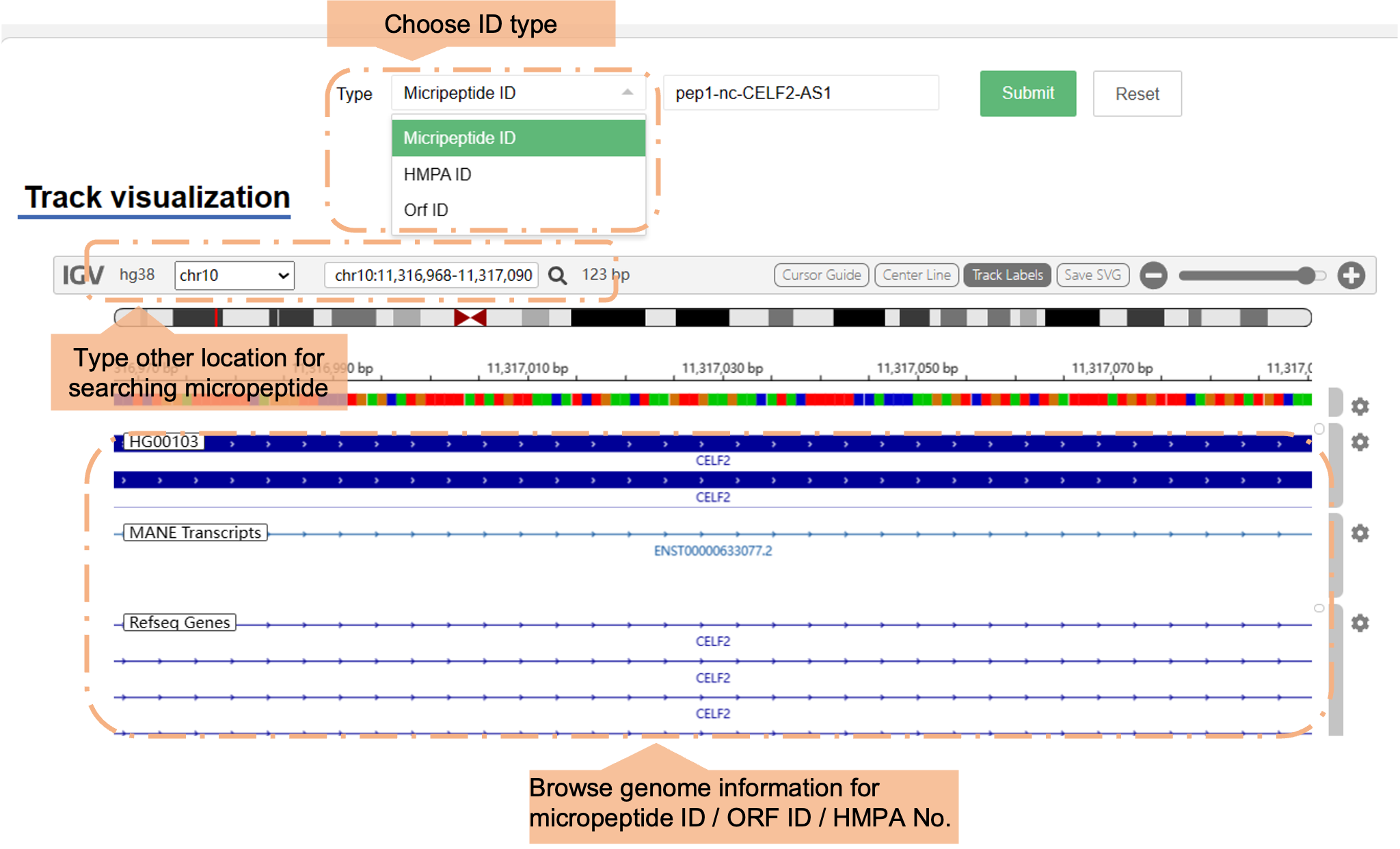
View micropeptide genome tracks directly in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This page offers a variety of HMPA datasets for download. Each dataset's name and description provide a description of its content. Data may be downloaded in zip or original format by users.

 Aifu Lin (linaifu@zju.edu.cn)
Aifu Lin (linaifu@zju.edu.cn)